3D laser scanning has significantly impacted manufacturing and engineering processes since its release. The 3D scanning market has experienced significant growth in recent years, reaching a market size of approximately $6.7 billion in 2023 (MarketsandMarkets). This momentum is expected to continue, with projections suggesting that the market will reach $13.3 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 7.9% (Market Research).
This expansion is fueled by advancements in 3D laser scanning technology and its increasing applications across the automotive, aerospace, and healthcare industries.
But what precisely is 3D laser scanning, and why is it regarded as one of the most innovative technologies available in engineering and construction today?
Let’s dive into the blog and explore the applications of 3d scanning.
📍 How Can 3D Laser Scanning Benefit Your Project?
From construction to heritage preservation, Survey2Plan delivers high-precision 3D scanning for every industry. Let’s discuss your needs!
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
What is 3D Laser Scanning?
3D laser scan is a modern measurement technology that employs laser scanners. It uses 3D point cloud data from an object’s surface to build an exact depiction of a structure.
In contrast to conventional surveying techniques, 3D laser scanning can capture even the most minor features of a structure. This data is then produced using a 3D point cloud survey to create as-built 2D drawings and 3D BIM models that can be utilized for various purposes.
3D Laser Scanning Applications
Here are some of the 3D laser scanner applications:
1. Building Renovations
The details captured by the 3D laser scanning document of a building are as follows:
- Exact layout
- Dimensions
- Locations of architectural, structural,
- MEP features walls, windows, doors, stairs, roofs, railings, exposed columns, beams, equipment, piping, and ducts.
The technology provides engineers and contractors with accurate point clouds that can be exported and created into 3D BIM models and 2D CAD drawings, ensuring that planned renovations blend perfectly with the building’s original architecture.
Identifying potential conflicts or clashes early in the planning process is possible by superimposing prospective renovation plans onto the 3D scan data.
3D laser scanning offers thorough as-built data for any site, whether you’re remodelling a stadium, theatre, historic building, church, school, etc. This adds value to the planning, design, and execution phases of any rehabilitation project.
2. Architectural and Civil Surveying
3D laser scanning aids architectural design by delivering accurate existing conditions to create design models, monitor construction progress, and verify as-built accuracy.
The accurate results allow technology for accurate design models, construction monitoring, and as-built verification. They also allow for exact documentation of sites or buildings, with as-built models reaching 6mm precision and point clouds reaching 2-4mm accuracy.
Laser scanning supports civil engineering by enhancing Building Information Modelling (BIM) with accurate 3D infrastructure models, such as roads and bridges. It also provides detailed elevation data for urban topography, aiding site development, road design, and drainage planning.
3. Maintenance, Retrofitting, or Expansion of a Power Plant
As power plants evolve to meet changing regulatory requirements or adopt new technologies, retrofitting existing infrastructure is often necessary.
3D laser scanning provides exact and detailed depictions of the plant’s as-built state, complete with structural elements, machinery, pipelines, boilers, generators, turbines, pumps, condensers, heat exchangers, and more.
This thorough documentation is a reliable guide for maintenance, retrofitting, and potential expansion initiatives. Engineers can plan new designs around existing infrastructure using precise 2D CAD drawings and 3D building information models (BIM) to minimise conflicts and interferences.
Engineers and maintenance staff can virtually tour the plant using 3D laser scanning without entering potentially dangerous regions. By identifying areas prone to corrosion, wear, or structural damage, you can create proactive maintenance schedules that reduce unscheduled downtime and extend the lifespan of crucial components.
Discover More: 3D Laser Scanning for Industrial Plants
4. Reverse Engineering
As its name suggests, the method disassembles an existing product to ascertain its operation. It carefully examines the materials, construction, geometry, mechanism, power delivery, and engineering design.
Reverse engineering shows the designer’s intent and is used to duplicate the product or create an enhanced version. Creating something based on an existing product is more accessible than starting from scratch.
When a product or design’s original CAD drawing is unavailable or inaccessible, 3D scanning provides a comprehensive overview of the item in question.
You can turn the scan data into a CAD file for engineering and construction analysis, seizing surface details such as measurements and primary specifications.
5. Forensics
3D laser scanning is widely used by law enforcement agencies worldwide for accurate onsite documentation. It enables the creation of detailed 3D models for:
- Crime scenes
- Bullet trajectories
- Bloodstain pattern analysis
- Accident reconstruction
- Bombings
- Plane crashes, and more
Investigators can use a 3D scanner affixed to a drone in conjunction with traditional cameras to obtain an advantageous perspective and capture intricate details from crime scenes.
This approach helps understand the sequence of events, enabling investigators to recreate potential scenarios and reconstruct the crime digitally virtually to test theories.
6. Obtain 3D Mesh Models for Films and Games
3D laser scanning produces detailed point clouds that can be converted into high-resolution mesh models (.fbx, .stl, .obj, .ply), which capture the fine geometry of objects like buildings, cars, and statues.
These meshes are ideal for viewing in CAD environments, offering a precise and volumetrically accurate alternative to point clouds.
This technology is widely used in industries requiring high image quality and detail, such as architectural visualization, product design, and the film and video game industry.
3D scanners create digital replicas of living things and environments faster than traditional modelling methods for films and games. This allows artists to manipulate and alter these assets using CGI for enhanced realism and creative flexibility.
7. Archaeology
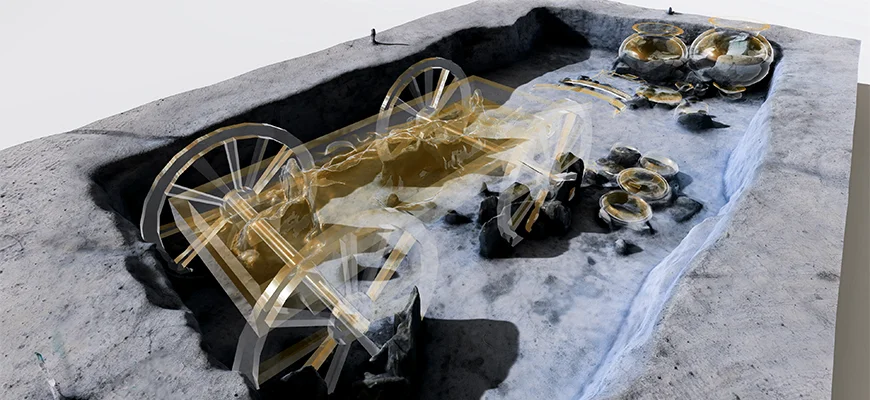
8. Architectural Heritage Preservation
Large-scale building CAD models are required for documentation, restoration, or remodelling projects.
3D scanning makes drawing the CAD plan simple when restoring a historic building’s architectural details, style, and designs to their original standards.
Scanning the entire structure rather than measuring each window, façade, beam, and ornament is easier.
Read More: 3D Laser Scanning for Heritage
9. Collecting Geospatial Data
3D laser scanning is instrumental in collecting geospatial data for various applications.
Aerial LiDAR and Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) combined with laser scanning allow experts to build precise 3D models of infrastructure, topography, and landscapes.
Geospatial mapping, environmental analysis, and urban planning depend on this data.
10. Documentation and Archiving
3D scanners help preserve history by capturing delicate artifacts and fossils into 3D digital form. Non-contact 3D scanners, such as structured-light systems, are especially great for this type of application because they capture the object without causing any disturbance to the original.
This technology allows museums to digitally archive collections and share them with anyone, anywhere in the world, through computers.
Advantages of 3D Laser Scanning
Laser scanning offers the following advantages:
- Cost-efficient
- Obtain accurate point clouds, 2D CAD drawings, and 3D BIM models
- Manual Labour Reduction
- Real-Time Data Verification
- Reflector less Technology
- Fast and efficient
Disadvantages of 3D Laser Scanning
The disadvantages of 3D laser scanning are as follows:
- The sensitivity of scanners to certain situations, including hot or low temperatures
- restricted reflection surface coverage
📍 Precision, Speed, and Reliability – All in One Scan!
No matter your industry, Survey2Plan’s 3D laser scanning services provide the data you need to succeed. Get in touch now!
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
Conclusion
Accurate measurements are essential to prevent costly errors, rework, and unexpected changes. Survey2Plan’s 3D laser scanning services provide precise site documentation.
Our skilled team of surveyors uses top-tier laser scanners to capture the intricate details of exterior and interior spaces.
Ready to see your project in a new dimension? Let Survey2Plan bring your vision to life.
Contact us to learn how 3D laser scanning can benefit your business.




