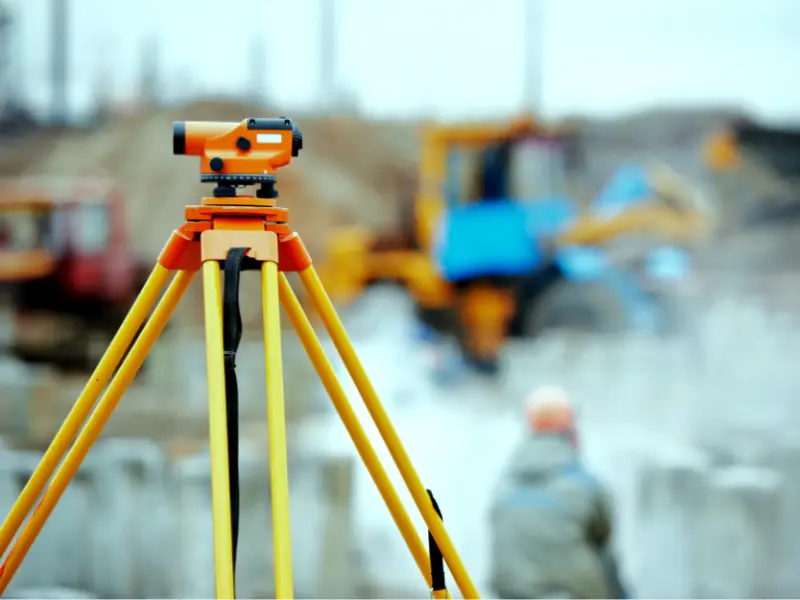
A point cloud survey is a method used to collect precise information about physical spaces and built structures. The data is then pieced together to create detailed visual representations of the environment. This approach has become increasingly popular in the architecture and construction sectors because it allows for quick interpretation of critical information. With clearer data in hand, teams are able to make better decisions, faster.
If you’re unfamiliar with how a 3D point cloud survey works, or what kind of equipment is involved, this guide breaks it down. We’ll also touch on how costs are calculated so you can decide whether it’s the right choice for your next project.

What is Point Cloud Technology?
Point cloud technology involves using high-end laser scanners to capture spatial data from real-world environments. Each scanner reads its surroundings and records numerous data points. These points collectively recreate a digital version of the scanned space, point by point.
As the scanner moves from one position to another, it captures surfaces from every angle. Each scan location produces a set of data points, which are then aligned and registered to create a cohesive model. This registration process is followed by exporting the data into modelling software. Depending on the end goal, the software can produce several digital outputs such as 2D plans, 3D models, or BIM-ready files.
The level of detail and overall accuracy of point cloud outputs can vary significantly. The final product can be tailored to measure accuracy within a few millimetres or, in some cases, several meters. The more data collected, the higher the potential accuracy. However, for smaller or less detailed projects, gathering extensive amounts of data isn’t always necessary.
This makes it important to assess your project requirements ahead of time. If your design doesn’t require pinpoint precision, you can save both time and money by opting for a lower-detail survey.
What Are the Benefits of Point Cloud Laser Scanning Surveys?

The introduction of point cloud laser scanning was a major leap forward for the surveying industry. Compared to traditional methods, these surveys bring a host of advantages:
- A single scan session can collect a wide range of measurements and spatial data in one go.
- The accuracy is impressive, enabling professionals to build detailed technical drawings or 3D models that support complex design and engineering work.
- Existing structures can be visualised in 3D, which is incredibly useful for projects involving heritage buildings or large-scale construction.
- Digital scans are easy to share with clients, contractors, and stakeholders meaning fewer people need to visit the site in person.
- Surveys can reveal structural issues or safety risks early on before they become serious problems.
- Scanning works even in challenging environments, including underground or low-light areas, making it ideal for mining surveys and similar projects.
What Equipment Is Used in Point Cloud Surveys?
A wide range of laser scanning tools are available, but a few names have become particularly well-known within the industry for their reliability and precision. These include:
- FARO Focus
- Leica Geosystems
- Trimble
- Z+F IMAGER
- Topcon
Each of these devices has different strengths. The choice of equipment depends on the size of the site, required accuracy, and intended use of the data.
What Factors Affect the Price Range of Point Cloud Survey
If you’re looking into using a point cloud survey on your next project then you’ll need to know how the finances work. One of the biggest benefits of using these surveys is that they help bring the overall costs of projects down but by how much?
Project scope and complexity
Area size and scan density
Data processing and required deliverables
Once the on-site data collection is complete, the data needs to be processed into the project’s required deliverables. Processing a point cloud survey is usually a two-stage process:
The first stage involves a process called point cloud registration, where a complete point cloud model is accurately assembled from each individual scan position. This data is then exported into a comprehensive point cloud of the building, structure, or site. Projects with a large number of scan positions or higher-density scans will take longer to register and export. Some projects will only require the point cloud model and will be delivered at this stage.
One of the biggest advantages of a point cloud survey is the variety of deliverables that can be produced from the on-site data. The second stage of processing is where the point cloud is converted into the required deliverables for the project, such as architectural drawings or a Revit model. This part of the process varies based on the project requirements, with some deliverables requiring more time and resources to produce than others.
Accessibility and safety
Site accessibility and safety can also impact point cloud survey pricing. Difficult-to-reach areas, such as remote locations or high-rise buildings, may require special equipment like drones or more powerful scanning equipment, adding time and expense. Additionally, obstacles like dense vegetation or confined spaces may require additional effort and planning.
Safety considerations also play a crucial role. Hazardous environments, such as active construction zones or industrial areas, require additional safety protocols, training, and possibly insurance. Obtaining necessary permits and ensuring compliance with safety regulations may also add administrative costs and time to the project.
How Much Does a Point Cloud Survey Cost?
General Price Ranges
For small, straightforward projects such as scanning a single room or a small residential property, the cost typically starts at around £250 to £500. These surveys require minimal time on-site and involve basic data processing. Mid-sized projects, such as scanning an entire house, a commercial office space, or a small industrial site, generally fall within the range of £500 to £1,500. These projects require more scan positions and processing time to ensure accurate results.
For large or complex projects such as heritage buildings, industrial plants, multi-story commercial structures, or infrastructure sites the cost can range anywhere from £1,500 to over £10,000. These projects demand advanced equipment, multiple scanning sessions, high-density data collection, and extensive processing to create usable 3D models or CAD drawings.
What Determines the Final Price?
While the size of the project is one of the most obvious cost factors, other elements contribute significantly to the final price. The level of detail required is a major factor in higher-density scans, which capture more intricate details, take longer to complete and process, increasing costs. Additionally, the type of deliverables you need plays a big role. If you only require a raw point cloud file, the cost will be lower than if you need fully developed 2D CAD drawings or a 3D Revit model, which require additional time and expertise.
Accessibility also impacts pricing. If a site is difficult to reach, such as a remote location, a high-rise building, or an area with safety hazards, additional resources, permits, or equipment may be required, leading to higher costs. Industrial sites or areas with complex layouts may need more scan positions, adding further to the price.
Finally, data processing time is a significant cost driver. The more scans taken, the longer it takes to process and align the data into a complete, accurate model. If a project demands high accuracy and detailed outputs, extra post-processing work is required, which increases the overall cost.
What Types of Projects Require Point Cloud Laser Scanning Surveys?
Heritage and Historic Building Surveys
Preserving historic and heritage structures demands extreme precision without risking damage to delicate features. Laser scanning offers a non-invasive way to digitally document these buildings in fine detail, supporting conservation, restoration, and historical research.
English Heritage commissioned a full laser scan of Stonehenge, uncovering previously unseen features and helping guide long-term preservation efforts. Similarly, PB Grassl architects digitally documented a 5th-century church in Bavaria, recording every intricate architectural detail necessary for accurate restoration work.
Measured Building Surveys for Commercial Properties
For commercial properties, accurate measurements are critical when planning redevelopment, refurbishment, or space optimization. Point cloud surveys create a precise base for CAD drawings, 3D models, and facility management systems.
In Sheffield, a commercial building covering over 10,750 square meters was surveyed using point cloud technology. Scene3D provided detailed CAD outputs that enabled architects to develop reliable and cost-effective redevelopment plans.
Construction and Infrastructure Projects
Major construction and infrastructure developments often involve complex designs and tight schedules. Laser scanning ensures that every phase—from foundation laying to final inspection—is monitored for accuracy, helping catch deviations early and supporting quality assurance.
Across Boston, point cloud laser scanning was used to survey over 130 schools, providing facility managers with precise as-built models. This data proved crucial for maintenance planning, energy upgrades, and future renovation projects.
Industrial Facilities and Plant Surveys
Industrial plants and manufacturing facilities are dynamic environments where changes must be documented precisely for operational efficiency, asset management, and compliance. Point cloud surveys help create up-to-date digital twins that support ongoing facility upgrades and expansions.
In Kentucky, Arrival 3D scanned an industrial facility, producing detailed 3D models. These digital outputs were used for space planning, optimizing workflows, and managing future asset installations more effectively.
Monitoring Climate Change and Natural Sites
Environmental monitoring demands repeatable, highly accurate measurements over time to study changes in natural features like forests, glaciers, and riverbanks. Laser scanning provides scientists with reliable datasets to support climate change research and conservation initiatives.
Environmental scientists used point cloud laser scanning to monitor Alpine glaciers, capturing detailed data about glacial movements. This information helped researchers better understand the impacts of climate change and contribute to long-term environmental planning.
Conclusion
At Survey2Plan, we take pride in delivering high-quality survey data that helps you build with confidence. Whether you’re planning a renovation, preparing for construction, or simply need accurate records of a structure, our team is ready to help.
From measured building surveys to full 3D laser scans, we provide services tailored to your specific needs. Want to learn more about what we can offer? Give us a call at 0161 531 6641 or email us at info@survey2plan.com.
We’re here to answer your questions, walk you through the process, and even provide a free quote no obligation.




