Being a property owner entails many different duties. The most important part of this is knowing what’s underneath your property. Ground penetrating radar scans and other utility studies should be taken into consideration when thinking about remodelling or relocating to a new property. It is impossible to overstate the benefits of having a thorough understanding of the subsurface structures, utilities, and any dangers on your property.
Surveys using Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) are useful in this situation. From identifying buried utilities to revealing historical secrets and supporting environmental evaluations, this blog will discuss the benefits of integrating GPR scans into your property management plan. Being a property owner is already stressful enough, but you must deal with unforeseen circumstances because you neglected to evaluate your property’s sublevels.
Read More: Importance of Utility Surveys
📍 Worried About What Lies Beneath? Get Clarity with GPR Surveys!
Uncover hidden utilities and subsurface features with Survey2Plan’s advanced Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) technology.
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
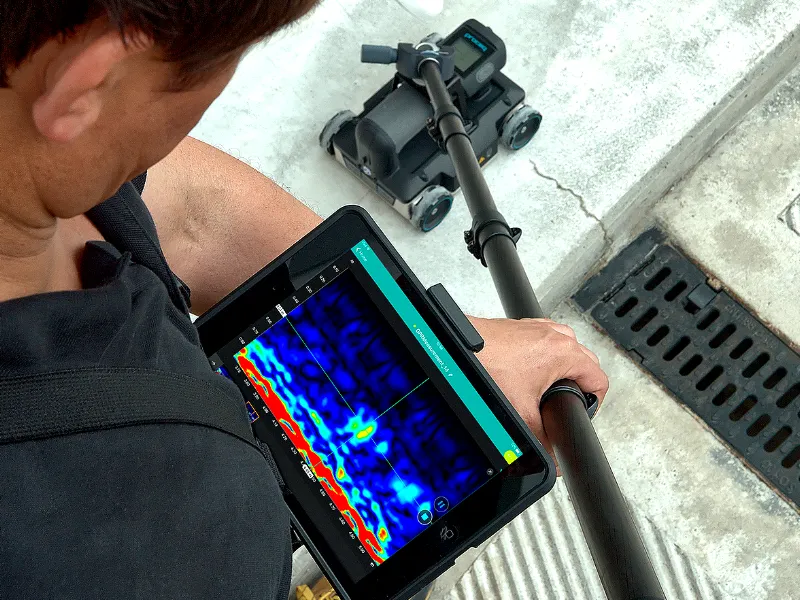
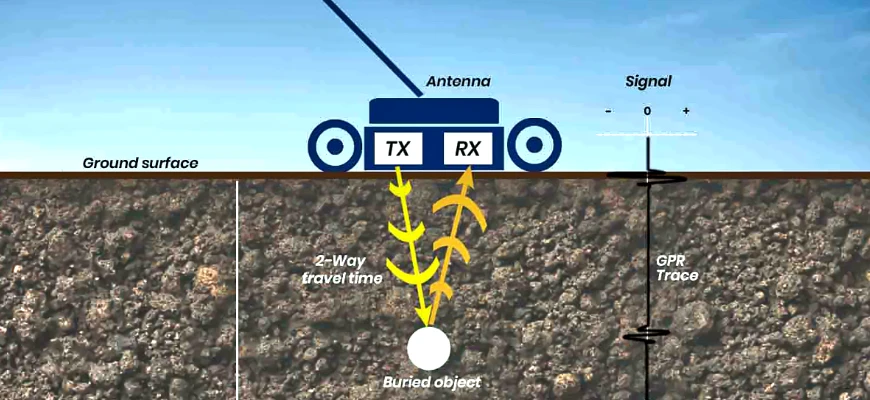
Ground Penetrating Radar
Firstly, let’s define Ground Penetrating Radar surveys.
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a non-intrusive geophysical technique utilizing radar pulses for subsurface imaging, widely applied in surveying underground utilities like concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables, or masonry.
GPR is appropriate for various media, including rock, soil, ice, water, pavements, and structures, because it operates in the microwave band of the radio spectrum, emitting electromagnetic radiation and capturing reflected signals.
Similar to seismology but using electromagnetic energy instead of acoustic energy, GPR uses high-frequency radio waves (10 MHz to 2.6 GHz) to analyse return signals to detect subsurface objects, changes in material properties, voids, and fissures.
Why Do I Need A Ground Penetrating Radar Survey At My Property?
Now, picture yourself standing outside your house.
On the surface, everything seems peaceful, but have you ever wondered what’s going on underneath?
Important information that directly affects the safety, value, and peace of mind of your home may be hidden beneath the surface of your land.
Here is where a Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) study is useful, not just for homeowners but also for building and development projects.
Your regular activities are supported by concealed wires, pipes, and possibly dangerous materials beneath the surface. An effective and non-invasive way to get a thorough picture of these hidden components is using a GPR survey.
Let’s examine the advantages of having a survey completed on your home and how it may provide you with a piece of mind.
Explore More: Construction Benefits Survey
Benefits of Ground Penetrating Radar
Starting Point
Ground-penetrating radar is a great tool to have on hand throughout a construction project. However, a GPR survey is most effective when conducted before any construction. The project will proceed much more smoothly if utilities and other potential obstacles are located and identified in advance.
Knowing what you’re dealing with underground makes building around these items much simpler. In certain situations, utilities may need to be moved or rerouted. By being aware of these possible hazards in advance, you can make sure that once construction begins, projects proceed smoothly.
No Need for Excavation
Not too long ago, there were just two methods available to construction workers for identifying subterranean services and items.
They could refer to utility maps or schematics, both of which are frequently erroneous or lacking information. Construction operations may uncover unknown items, such as unmarked graves or even archaeological discoveries. Such findings have the power to halt a building project in its tracks.
The alternative is to just begin digging. Excavating is also expensive, both financially and in terms of time, as anyone involved in construction is aware.
Thankfully, GPR provides a method for construction workers to scan sites without breaking ground, avoiding both of these situations. Schematics and utility maps are also used as references rather than rule books because of GPR’s great accuracy.
Keep Your Team Safe
Prevent Costly Damages
In addition to being risky, not knowing what’s beneath the surface before excavation can be expensive. Project delays may arise from mishaps brought on by damaged utilities. In the worst situations, these incidents may result in costly damage to building supplies and equipment.
You may assist in guaranteeing a wise investment and a seamless project from start to finish by utilising GPR to map and locate every subsurface object before the project starts.
Reliable in Any Environment
Unlike other underground locating methods, GPR isn’t limited to specific materials or environments. You can use it in the planning phases of construction to locate any kind of underground object in:
- Soil
- Rock
- Asphalt
- Concrete
And during construction, you can use GPR to help locate rebar in cement structures.
Related: Underground Utility Surveys
Applications of Ground Penetrating Radar
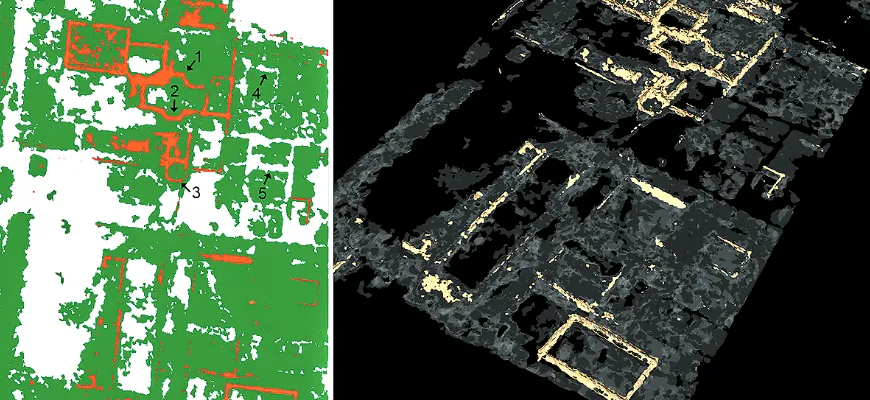
The applications of Ground Penetrating Radar include the following:
- Utility detection in infrastructure and building.
- Archaeological research to map artifacts beneath the surface.
- Ecological evaluations to identify subterranean storage tanks or pollutants.
- To investigate subsurface geology, geological surveys are used.
- Pavement evaluation for infrastructure upkeep.
- Concrete inspection is used to find fractures or cavities in the concrete and determine where the rebar is placed.
Limitations of Ground Penetrating Radar
The limitations of Ground Penetrating Radar include the following:
- Under some circumstances, this radar’s deep penetration is limited.
- Complex subsurface habitats present several interpretive issues.
- In conductive materials, high-frequency impulses may be attenuated.
- Need knowledgeable operators to analyse data accurately.
📍 Precision You Can Trust – Advanced GPR Surveys by Survey2Plan
Ensure safety, efficiency, and accurate data collection with our cutting-edge GPR solutions. Contact us today!
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
Conclusion
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a powerful, non-intrusive tool that provides crucial insights into the subsurface, making it an essential asset for property owners, builders, and surveyors. By detecting hidden utilities, preventing costly damages, and ensuring safety, GPR surveys help streamline construction and renovation projects while minimizing risks. Its versatility across various environments and applications—from utility detection to archaeological research—further highlights its value. While GPR has some limitations, its benefits far outweigh the challenges when operated by skilled professionals. Investing in a GPR survey ensures informed decision-making, protecting both your property and those working on it.




