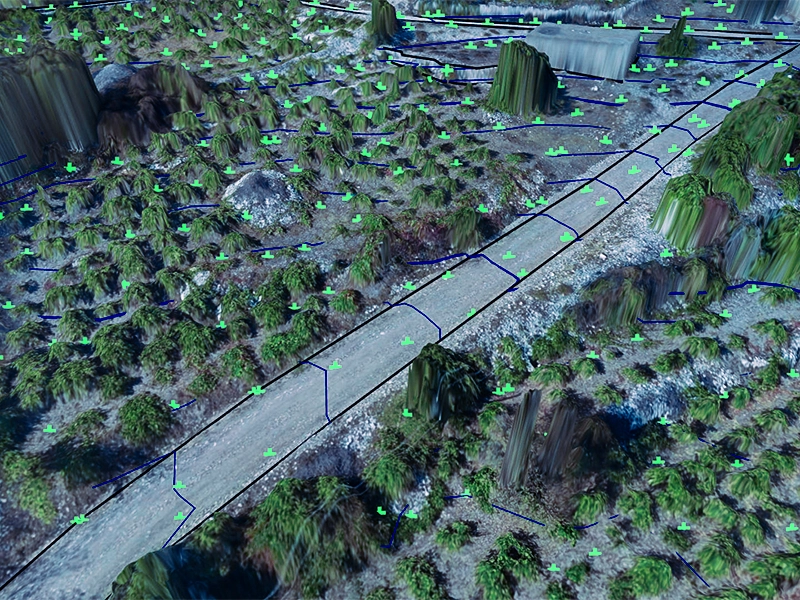


Topographic surveys are crucial resources for comprehending a landscape’s traits and features. They offer vital information on an area’s natural and man-made features, facilitating well-informed decision-making in various domains, such as environmental preservation, urban planning, and development.
📍 Planning a Development Project? Start with a Precise Topographic Survey!
Survey2Plan provides detailed, high-accuracy surveys to support seamless land assessment and planning.
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
What is a Topographical Survey?
Why Topographic Surveys are Important?
Topographic surveys are crucial in many industries. They help make better planning and design possible in the building industry by identifying potential risks, drainage patterns, and site boundaries. Topographic surveys are essential for urban planning because they offer valuable land use and development information, ensuring that projects meet community and environmental objectives. In environmental protection, these surveys also support sustainable development practices by helping to evaluate the ecological variety and the effects of human activity on natural environments.
Who Needs a Topographic Survey?
Several key stakeholders benefit from topographic surveys, including:
- Real Estate Developers: Require accurate data for site selection, planning, and development of residential and commercial properties.
- Architects: Use survey information to design structures that integrate harmoniously with the surrounding environment.
- Engineers: Depend on topographic data to inform infrastructure design, ensuring stability and compliance with regulations.
- Environmentalists: Utilize surveys to evaluate the health of ecosystems and assess the impact of development on natural habitats.
- Local Authorities: Need comprehensive topographic information to effectively manage land use, zoning, and public safety measures.
Types of Topography Survey
Topographical surveys come in several types, each offering specific insights based on the needs of a project. Here are the main types of topographical surveys:
2D Topographic Surveys
2D topographic surveys are frequently used for small projects like home gardening or straightforward civil works.
3D Topographic Surveys
2D surveys provide a comprehensive three-dimensional view of the land. They are helpful for intricate tasks where comprehending the shapes and differences in the landscape is essential.
LIDAR Survey for Topography
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) surveys are highly valuable for projects where dense vegetation obstructs the land surface.
Ground Penetrating System (GPS)
GPS topographical surveys are ideal for large, open areas like quarries, agricultural fields, or wind farms. They can be efficiently mapped using real-time, high-accuracy data from GPS technology.
Hydrographic Survey
A hydrographic survey maps the water’s surface beneath an object. Specialised hydrographic companies solely handle subsea projects.
Topographic Survey Costs
The cost of completing the survey varies depending on the demands, difficulties, and level of detail needed for the suggested site.
Basic Surveys: For smaller residential projects (e.g., gardens or single residential plots), costs can range from £500 to £1,500.
Medium-Sized Surveys: For larger sites (like commercial developments or multiple residential units), expect costs between £1,500 and £3,500.
Large or Complex Surveys: Depending on the site’s complexity, prices may range from £3,500 to £10,000 or more for extensive projects (such as industrial sites or large-scale developments).
Factors Affecting Survey Costs:
- Area Size
- Survey Complexity
- Equipment Used
- Level of Detail Required
Therefore, the best way to explain your survey requirements is to contact our staff directly. Then, of course, we’ll be able to provide you with a much more accurate price at no cost!
Fill out our form, call us, or email us today!
Essential Components of a Topographic Survey
-> Elevation Data
Elevation data is a digital representation of the Earth’s terrain. It can be represented using points such as x, y, and z or in gridded formats or rasters. It is collected using topographic surveying equipment, including GPS receivers, laser scanners, and total stations.
-> Contours
-> Survey Control Points
-> Natural Features
-> Man-made Features
Along with natural features, topographical surveying also help identify man-made features in a landscape. These man-made features can include roads, utilities, buildings, and other developed infrastructures. When surveyors have access to both natural and man-made features, it becomes easier for them to carry out the planning and development processes.
We would now like to discuss the process of conducting a topographical survey. We are sure you learned many things today, so let’s dive into the complexities of a topographical survey now!
How a Topographical Survey is Conducted?
1. Planning & Preparation
2. Data Collection
3. Data Analysis and Processing
The step of analysing the data and processing it allows going through raw data and then generating digital elevation methods (DEMs). The surveyors and other concerned individuals can then evaluate terrain characteristics by utilizing modern techniques and software.
4. Mapping & Reporting Processes
5. Data Management
📍 Need a Clear Picture of Your Land Before Construction?
Our topographic surveys provide precise site data, helping you make informed decisions and avoid costly errors.
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
Applications of Topographical Surveys
Due to their comprehensive mapping capabilities, topographic surveys are essential tools for various fields. Key applications include:
Construction: Assists in precise land measurements, slope analysis, and identifying potential hazards for safe project execution.
Urban Planning: Helps planners design sustainable, efficient city layouts, incorporating green spaces and transport links.
Environmental Studies: Supports impact assessments, monitoring changes in natural landscapes, and conserving ecosystems.
Real Estate: Aids property valuation and development planning by assessing land use potential and boundaries.
Historical Conservation: Captures detailed topography of historical sites, preserving cultural landmarks for restoration and research.
Equipment Used in Topographic Survey
- Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
- Total Station
- 3D Laser Scanner
- Unnamed Aerial Vehicle (Drone)
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Digital Level
- Data Processing Software
Benefits of Topographical Survey
Investing in your development is challenging, but a few key elements will help you achieve your goals. A rapid and precise topographic survey can considerably reduce the degree of risk.
A topographical survey gives you, your planning team, and the local government the extra details you need to understand the area you want to develop. Just as in many situations, information is power; thus, having the right information at the right time will help your project in many ways. Below are some of the key benefits that a topographic survey can bring to your project:
Reduce Risk with Accurate Data
Investing in a topographic survey early in your project helps avoid costly mistakes. The precise information gathered lowers the chances of running into unexpected issues, ensuring your project progresses smoothly.
Gain Valuable Insights for Better Planning
A topographic survey provides critical information about the land you’re developing. It provides details like site levels, boundaries, and nearby land features, allowing you and your planning team to make informed decisions and refine your designs before proceeding.
Prevent Costly Errors and Delays
Topographic surveys help you avoid expensive mistakes by identifying potential constraints early, such as unstable ground surfaces or trees that need protection. You’ll be able to adjust your plans well before submitting your planning application, saving time and reducing the risk of delays.
Improve Design and Construction Choices
A topographic survey provides a complete picture of the land, enabling better design decisions. The survey reveals key information about the site that can influence everything from the choice of foundation to drainage details. It ensures your development is built on solid, well-informed plans.
How to Read a Topographic Map?
- Scale: Topographic maps have a scale that indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. Understanding the scale is crucial for accurate navigation and planning.
- Legend: This section explains the symbols and colors used on the map, helping users identify land features, such as roads, rivers, and vegetation.
- Elevation: Each contour line is labeled with its elevation, typically above sea level. This information is vital for understanding how the land rises and falls.
- Symbols: Topographic maps use various symbols to represent features like buildings, trails, and bodies of water, providing a comprehensive view of the area.
How to Use Topographic Survey Data
Using Data for Design and Construction
The detailed data from topographic surveys is invaluable in construction. It enables architects and engineers to plan site layouts, design infrastructure, and develop foundations accurately. This data informs critical design decisions for site grading, drainage, and building positioning, thereby optimizing project efficiency and reducing potential construction errors.
Data Integration with Other Surveys
Topographic surveys often integrate with boundary, geological, and environmental surveys to create comprehensive site profiles. For example, a topographic survey combined with a geological survey provides data on both surface features and subsurface conditions, aiding in more informed planning and reducing construction risks.
Digital Tools for Further Analysis
Surveyors increasingly use digital tools, like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and GIS (Geographic Information Systems), to process and analyze topographic data. These tools help visualize land features in 3D models, offering insights into site planning and forecasting. Additionally, such technology allows for easy data layering and manipulation, making it easier for teams to simulate potential developments and analyze environmental impact.
📍 Precision Topographic Surveys for Informed Decision-Making
Avoid costly surprises—ensure your site is accurately mapped with Survey2Plan.
📞 0161 531 6641 📩 info@survey2plan.com 💬 Get a Quotation
Fast & Accurate Surveys | Trusted by Architects, Developers & Contractors
The Role of a Topographic Surveyor
A topographic surveyor collects data on land features, including contours, elevations, and boundaries, which is essential for accurate land development planning.
Choosing the Right Surveyor for Your Project
To select a topographic surveyor, consider:
Relevant experience in the project type.
- Accreditation and compliance with industry standards.
- Use of advanced tools for data accuracy.
- A strong portfolio and excellent client communication.
Typical Challenges and How Surveyors Overcome Them
Surveyors face obstacles like harsh weather, remote terrains, and sensitive ecosystems. They ensure accuracy and project continuity by using specialized equipment, preparing for adverse conditions, and adapting strategies.
Previous Post
← Preserving the Past with 3D Laser Scanning Technology